Spanish has about 360,000,000 million native speakers worldwide.
It has several major dialects which differ based on certain aspects of pronoun use, pronunciation, and verb conjugations as well as vocabulary. For instance the Spanish of Europe uses the informal pronoun tú much more often, along with vosotros and vosotras, which are nearly absent in the dialects of Latin America.
The Spanish of Mexico, the Caribbean, and the Andean regions of South America is generally considered by scholars to be more conservative because of its colonial history. It retains many features of the Spanish used in 16th and 17th century Spain, much how the English of North America has retained some older features of the language that have been lost in British English.
Many dialects in Latin American incorporate words from indigenous languages like Quechua and Nahuatl. Rioplatanese Spanish, which is spoken the countries surrounding the Rio Plata river basin - Argentina, Uruguay and Paraguay - has heavy influence from Italian and Portuguese due to immigration and cultural ties.
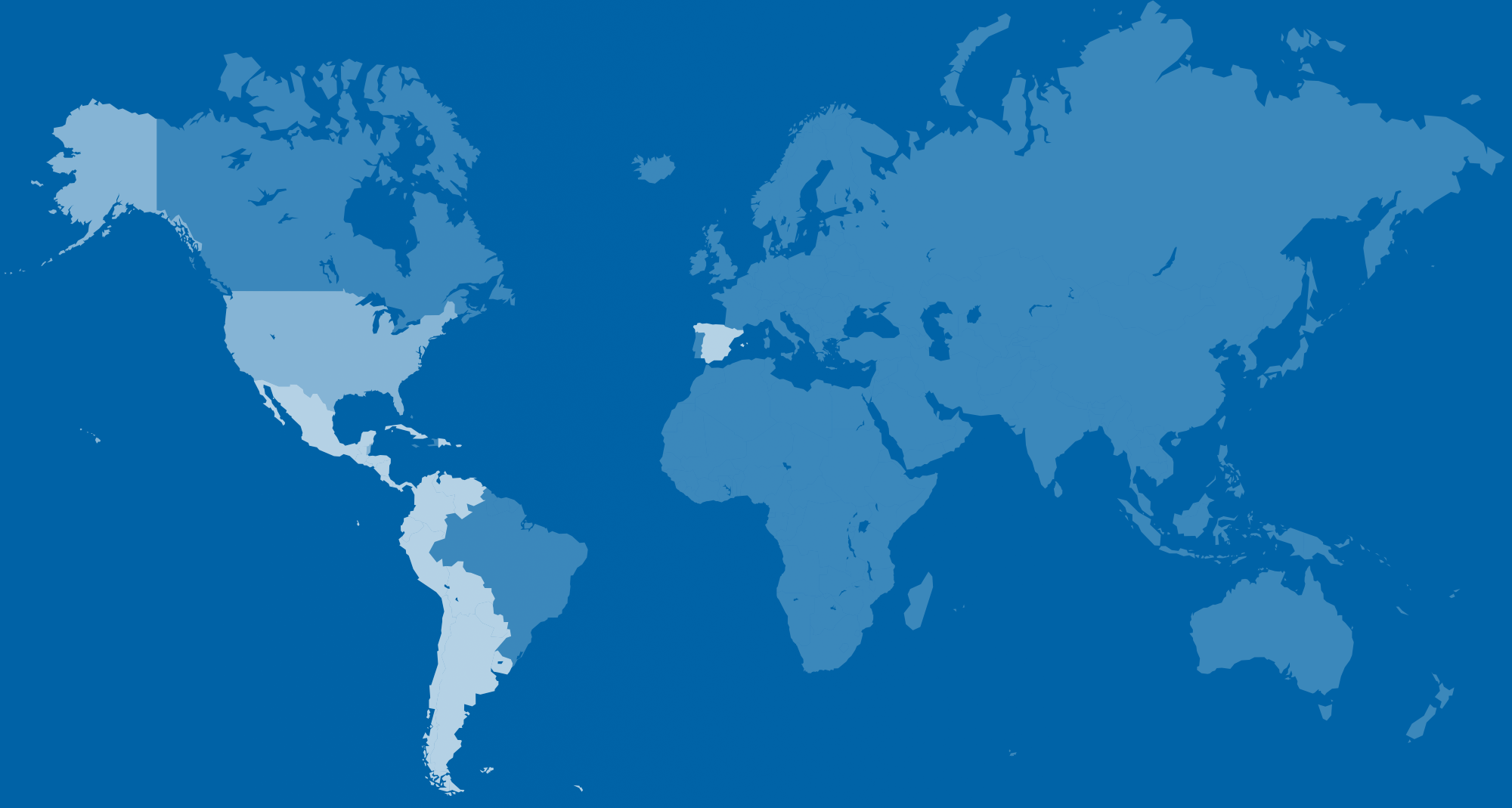
Countries where Spanish is spoken
Países donde se habla español
Dependent territories where Spanish is spoken
Territorios dependientes donde se habla español
Transnational organizations where Spanish is an official language
Organizaciones transnacionales que reconocen español como un idioma oficial
Regions where Spanish is spoken
Regiones donde se habla español
Related Lessons
Lecciones relacionadas



 French
French English
English Italian
Italian German
German Portuguese
Portuguese Hebrew
Hebrew Arabic
Arabic Russian
Russian Chinese
Chinese Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Dutch
Dutch







