Introduction
مُقَدِّمَة
Many world languages such as Spanish and German assign grammatical gender to nouns. While Arabic also does this, it takes it one step further and includes a grammatical gender aspect in verbs too. For instance when asking someone how they are, the phrase changes depending on whether the person is male or female:
How are you?
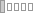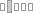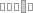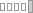
كيفَ حالُكَ؟
(kayfa Haloka)
Addressing to a male
كيفَ حالُكِ؟
(kayfa Haloke)
Addressing to a female
Moreover, the word "you" translates several different ways based on gender-specification. For instance, when addressing a singular male you use the word أنتَ (aanta) and أنتِ (aanti) with a singular female.
How are you?
كيفَ حالُكَ؟
(kayfa Haloka)
Addressing to a male
كيفَ حالُكِ؟
(kayfa Haloke)
Addressing to a female
Moreover, the word "you" translates several different ways based on gender-specification. For instance, when addressing a singular male you use the word أنتَ (aanta) and أنتِ (aanti) with a singular female.










 French
French Spanish
Spanish English
English Italian
Italian German
German Portuguese
Portuguese
Comments
التعْلِيقَات